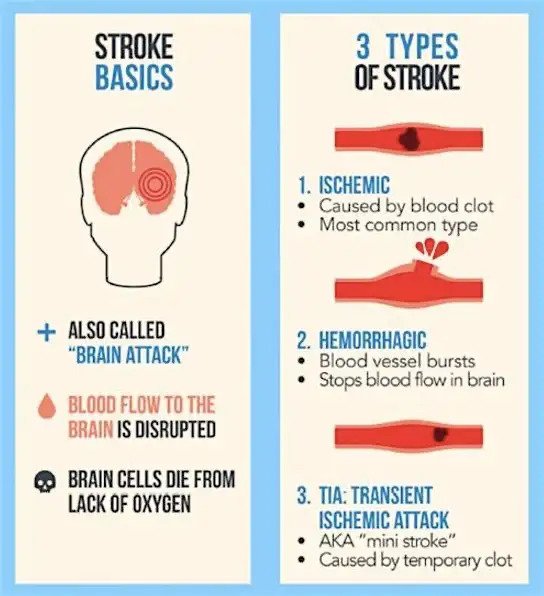
What is stroke?
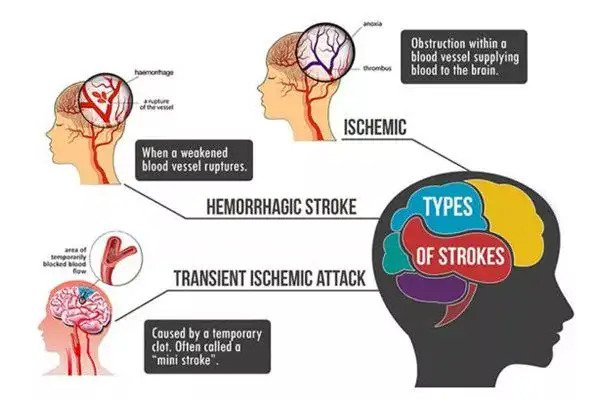
A stroke happens when the blood supply to one or more parts of the brain is reduced or completely blocked. The blockage may be temporary or permanent and it can be caused in two different ways:
- In ischaemic strokea blood clot obstructs the supply of blood to the brain
- In hemorrhagic strokea blood vessel bursts and bleeds into the brain
All parts of the brain need to have a good blood supply to work properly. When the flow of blood is restricted or stopped, vital nutrients and oxygen cannot reach the cells in the brain and they are damaged or die.
All parts of the brain need to have a good blood supply to work properly. When the flow of blood is restricted or stopped, vital nutrients and oxygen cannot reach the cells in the brain and they are damaged or die.
The effects on the body depend on which part of the brain is damaged and how long the blockage remains.
A stroke can affect movement, speech, thought processes and memory. It can cause paralysis in one or more parts of the body, or loss of control of bodily functions.
About 40% of people affected by stroke will have permanent symptoms that result in them needing special care.
Many people’s symptoms improve significantly following a stroke, but only about 10% of patients recover fully.
Anyone of any age can have a stroke, but there are some important risk factors.
The chance of having a stroke increases with age, for example. Certain ethnic groups are more at risk and a family history of stroke increases the chance that you may be affected.
There are also risk factors that we may reduce through lifestyle changes, such as making sure any high blood pressure is treated, eating a healthy diet low in fat and salt, stopping smoking and staying physically active.
How could stem cells treat stroke?
One reason that helping people recover from a stroke can be difficult is that stroke damages many different types of cells in the brain.
This means that, if we want to develop a therapy to replace lost or damaged cells, we need to:
- Learn to grow many different kinds of brain cells, or the appropriate type of stem cells to make the brain cells we need
- Show the cells we can grow work properly
- Understand how to enable these cells to organize themselves in same way as inside the healthy brain, recreating complex connections across different areas of the brain and joining the cells up with the brain’s blood supply these are huge challenges. Scientists have been working for many years on developing potential ‘cell replacement therapies’ for stroke and continue to do so.
However, researchers are also examining alternative ways to use stem cells in stroke treatment.
For example, stem cell research may be used in the development of new drugs that could stimulate the brain’s own repair mechanisms, including its own stem cells, to make the new cells that are needed for recovery.
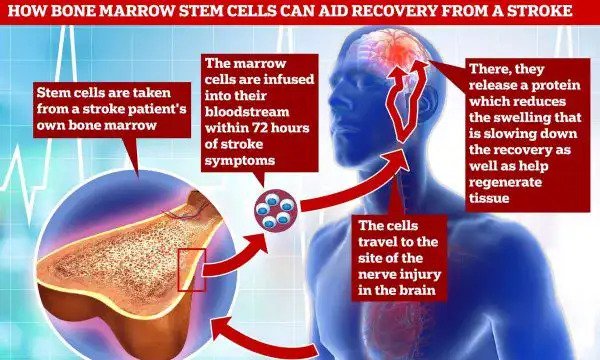
Mesenchymal stem cells and stroke
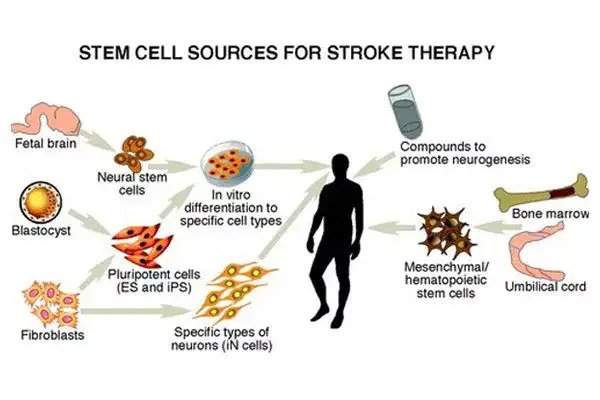
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are one of the most commonly used types of stem cell in clinical trials on stroke to date. They can be easily obtained and grown from a patient’s bone marrow and can produce fat, cartilage and bone cells.
Mesenchymal-stem-cell-like cells can also be derived from other sources such umbilical cord and adipose (fatty) tissue, though the exact identity and nature of these cells is still the subject of some scientific debate.

MSCs from bone marrow and cells obtained from adipose tissue have been injected into the brain or into a vein in the leg of rats with stroke-like brain damage.
In these studies, animals that received injected cells showed a decrease in the size of the damaged area of the brain compared to animals that were not given an injection.
The injected cells appear to move to the damaged area of the brain, but this is not thought to be essential for a beneficial effect since MSCs cannot make new brain cells. Instead, the researchers carrying out such studies think the injected MSCs produce and release substances that reduce inflammation and stimulate self-repair within the brain.