Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetes
With such a large and increasing portion of the world population affected by this disease there has been a significant amount of resources devoted to its treatments.
While treatment can control the symptoms and usually avoid the associated serious complications there is currently no cure for diabetes.
The overwhelming amount of success in treating animal models of diabetes with Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC’s) has led to a significant number of human clinical trials to do the same. There are 2 main ways this is happening.
The first way is that MSC’s are being evaluated for their safety and usefulness in directly treating the condition of diabetes.
The second way is that MSC’s are being evaluated for their safety and usefulness in treating the complications of diabetes such as diabetic ulcer.

Type 1 Diabetes:
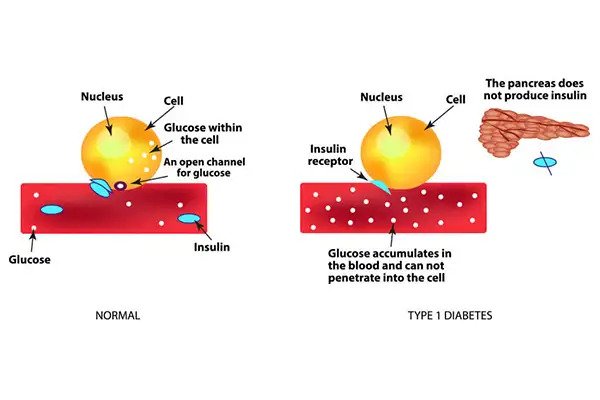
If you have type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. Your immune system attacks and destroys the cells in your pancreas that make insulin. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, although it can appear at any age. People with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day to stay alive.
It is not known exactly why the body immune system fights the b-cells and it causes Type 1 diabetes.
It´s assumed that this could have been caused by genetic vulnerability and certain environmental factors but there is no absolute clear reason why this happens.
Type 2 Diabetes:

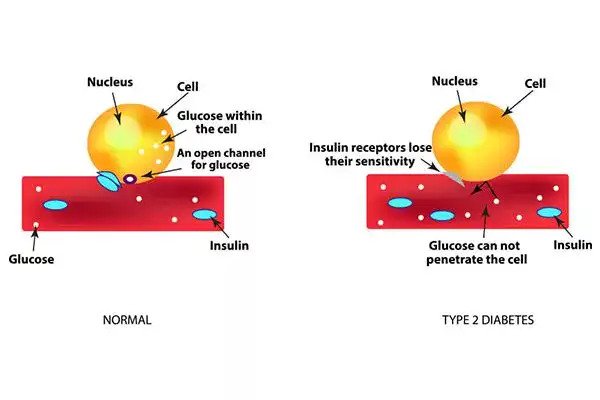
If you have type 2 diabetes, your body does not make or use insulin well. You can develop type 2 diabetes at any age, even during childhood.
However, this type of diabetes occurs most often in middle-aged and older people. Type 2 is the most common type of diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the cells resist insulin action and the insulin produced is not enough to overcome this resistance, the reason behind this resistance is also unknown but it is strongly assumed that obesity is directly linked to this type of diabetes.
Beneficial Actions of Stem Cells for Diabetes
- Protect and prevent remaining β-cells from dying (apoptosis)
- Promote beta cell function
- Transform into β-cells
- Regulating of the immune system (immunomodulation)
- Reduce inflammation (anti-inflammatory)
- Induce autophagic activity
- Prevent and reverse metabolic hormone resistance
- Regulate blood sugar levels
- Encourage existing cells to self-repair (autocrine effect)
- Encourage existing cells to adapt (plasticity)
Results Achieved with Stem Cell Treatment:
- Significant decrease in fasting blood sugars and the level of Hemoglobin A1C
- Significant decrease inflammatory markers such as C-Reactive Protein
- Measurable improvement in kidney function with a decrease in creatinine levels
- An improved capacity for physical activities
- An increased feeling of vitality with improved energy levels
- A reduced risk of complications
- Loss of neuropathy (numbness)
- Loss of pruritus (itchy skin)
- Loss of Nocturia (having to wake up from sleep to urinate)
- An increased libido
