What is erectile dysfunction (ED)?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to get or keep an erection firm enough to have sexual intercourse. It’s sometimes referred to as impotence, although this term is now used less often.
Occasional ED isn’t uncommon. Many men experience it during times of stress. Frequent ED, however, can be a sign of health problems that need treatment. It can also be a sign of emotional or relationship difficulties that may need to be addressed by a professional.
What causes an erection dysfunction (ED)?

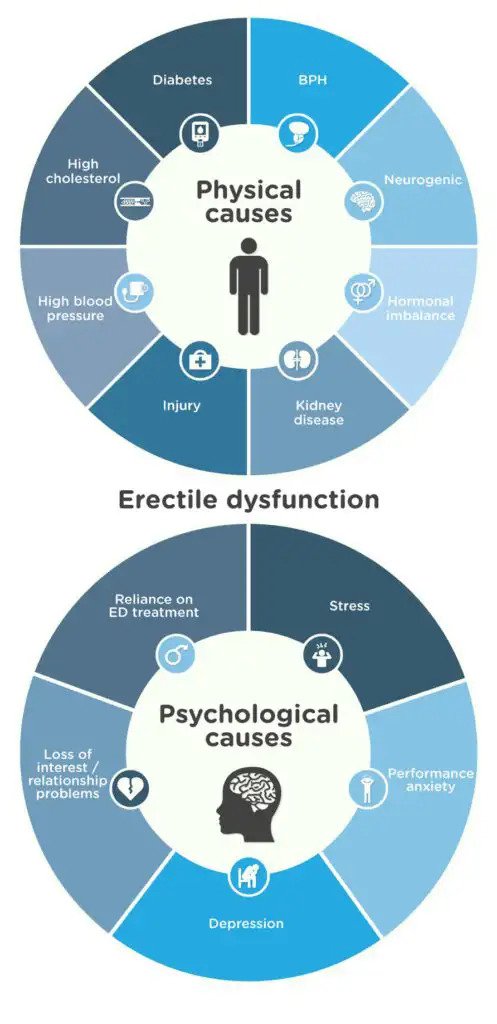
While previously, ED was believed to be primarily due to psychological causes, this is no longer the case. Currently, the vast majority of cases have been attributed to an underlying organic disease.
The most prevalent causes of erectile dysfunction are due to the effects of diabetes, post-surgical issues following prostate surgery and patients suffering from heart disease and high blood pressure.
ED affects nearly 10 percent of all men. It can present as an inability to achieve an erection or maintain an erection long enough to have intercourse or achieve orgasm.
Erection of the penis is a hemodynamic action in the tissue of the corpus cavenosum, the erectile tissue forming the bulk of the penis.
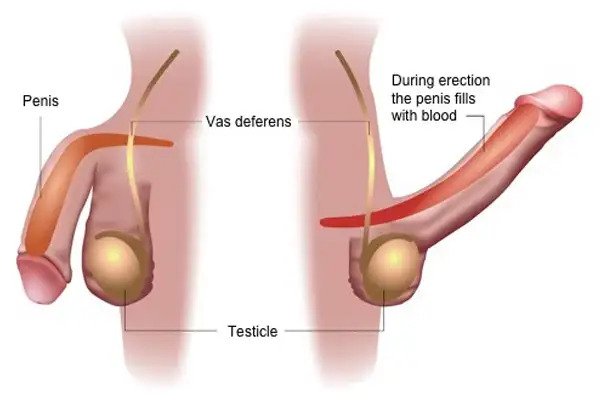
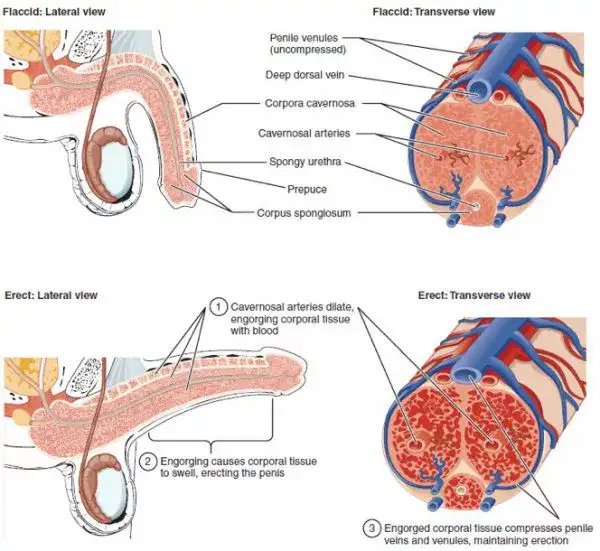
ED may result from the inability to fill the erectile tissue with blood, or failure to store the necessary blood in volume in the erectile tissue.
Stem cell therapies address the defects at all stages of the erectile process
There are many possible causes of ED, and they can include both emotional and physical conditions. Common causes include:
- cardiovascular disease
- diabetes
- hypertension, or high blood pressure
- high cholesterol
- obesity
- low testosterone levels or other hormone imbalances
- kidney disease
- increased age
- stress
- anxiety
- depression
- relationship problems
- certain prescription medications, such as those used to treat high blood pressure or depression
- sleep disorders
- drug use
- consuming too much alcohol
- using tobacco products
- certain health conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease or multiple sclerosis (MS)
- damage to the pelvic area through injury or surgery
- Peyronie’s disease, which causes scar tissue to develop in the penis
How Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction Work
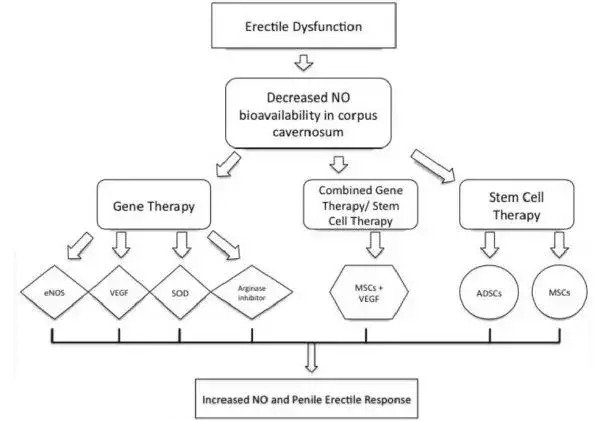
Stem cell therapy for the treatment of erectile dysfunction utilizes both the patient’s own stem cells and growth factors to achieve a natural male enhancement that helps regenerate erectile tissue and improve erections, sexual performance and penis size.
A combination of the patient’s own sources of these cell and growth factors are used to achieve maximum effect.
The largest reservoir of stem cells is found in adipose (fat) tissue. Besides adipose-derived cells, additional stem cells and growth factors are sourced from bone marrow concentrate. The procedure consists of two parts:
- The harvest of adipose-derived stem cells using a high-tech liposuction device to comfortably extract the fat tissue.
- Bone marrow is harvested from the iliac crest.
Once we extract the two components, they are processed in our lab through a centrifuge process.
The last step in the process is the virtually painless injection. The injection is expertly placed with a micro needle to the specific locations. The procedure does not require a general anesthetic; it only requires local anesthesia and light sedation.
